03. Write the Fetch Request
Write The Fetch Request
Ok, let's look at a sample fetch request, and then we'll make a fetch request for an image from Unsplash.
fetch('<URL-to-the-resource-that-is-being-requested>');So yeah…that's it. In it's smallest form, a Fetch request is just the fetch() function and a string to the resource that's being requested. It's just so short and easy to read (sigh I think I'm in love!). Let's take a peek at what a real request looks like:
fetch('https://api.unsplash.com/search/photos?page=1&query=flowers');If you try running this Fetch request on the console, then you should get a Promise returned to you.
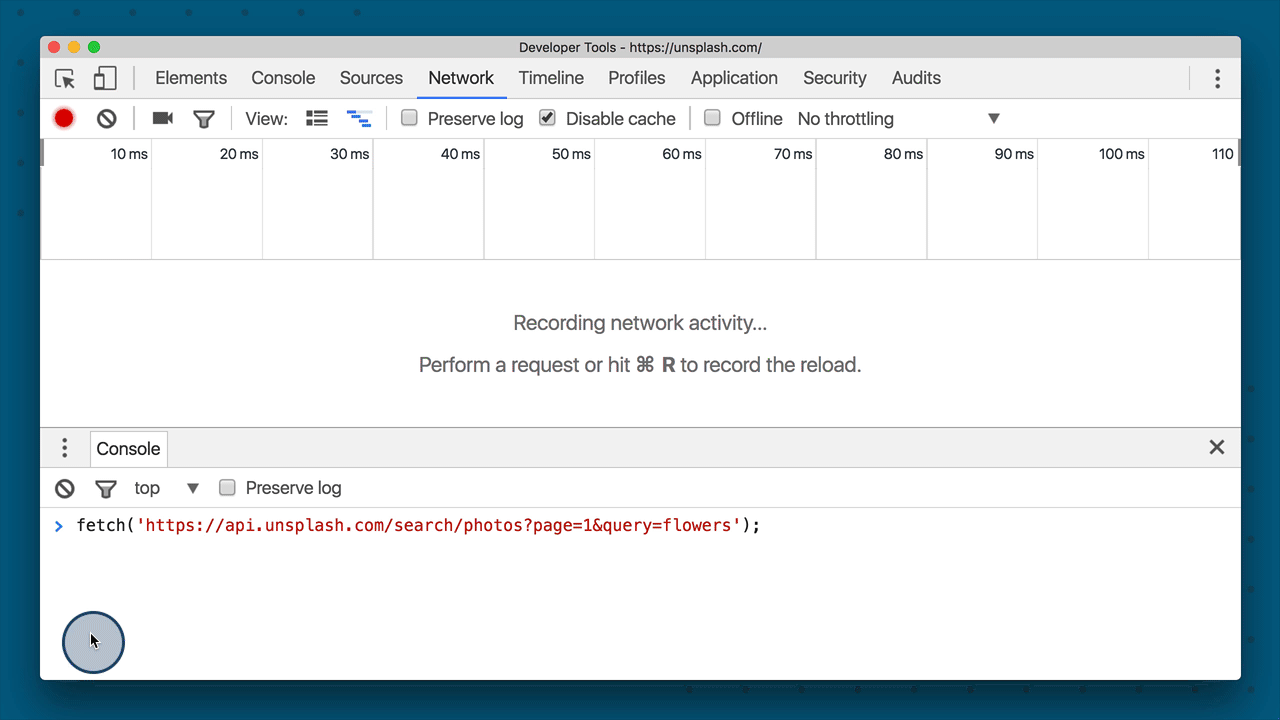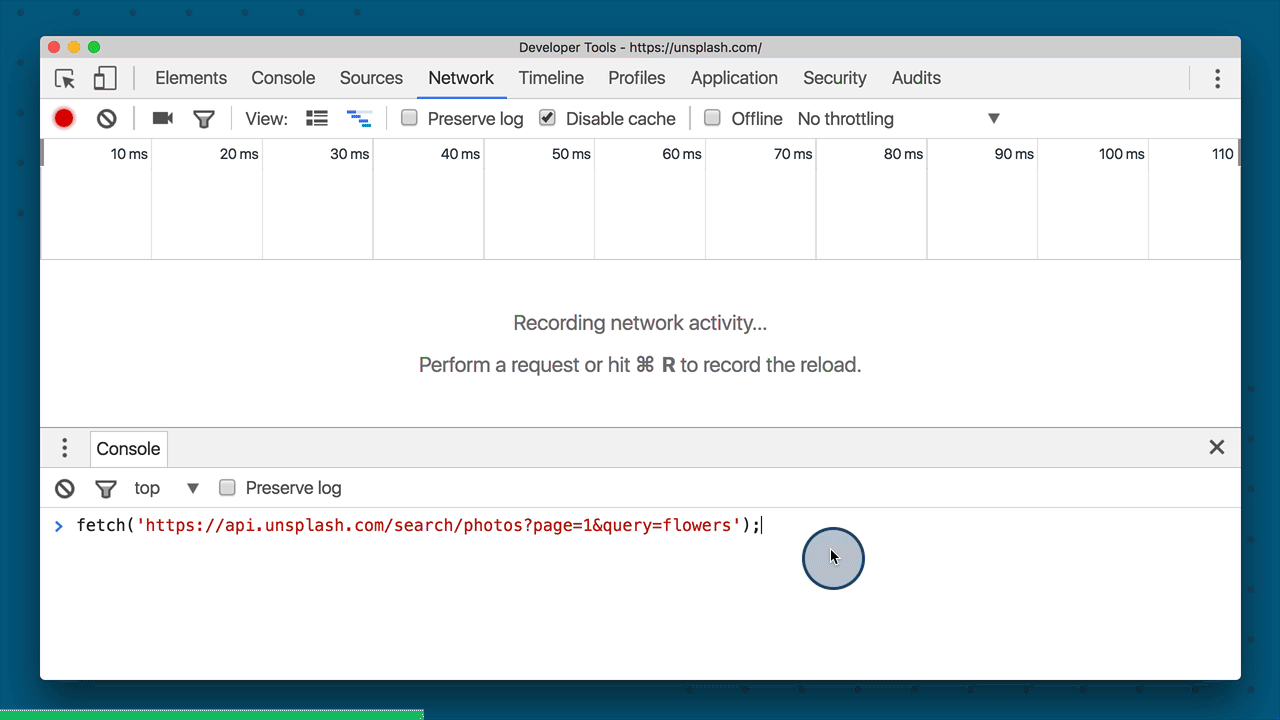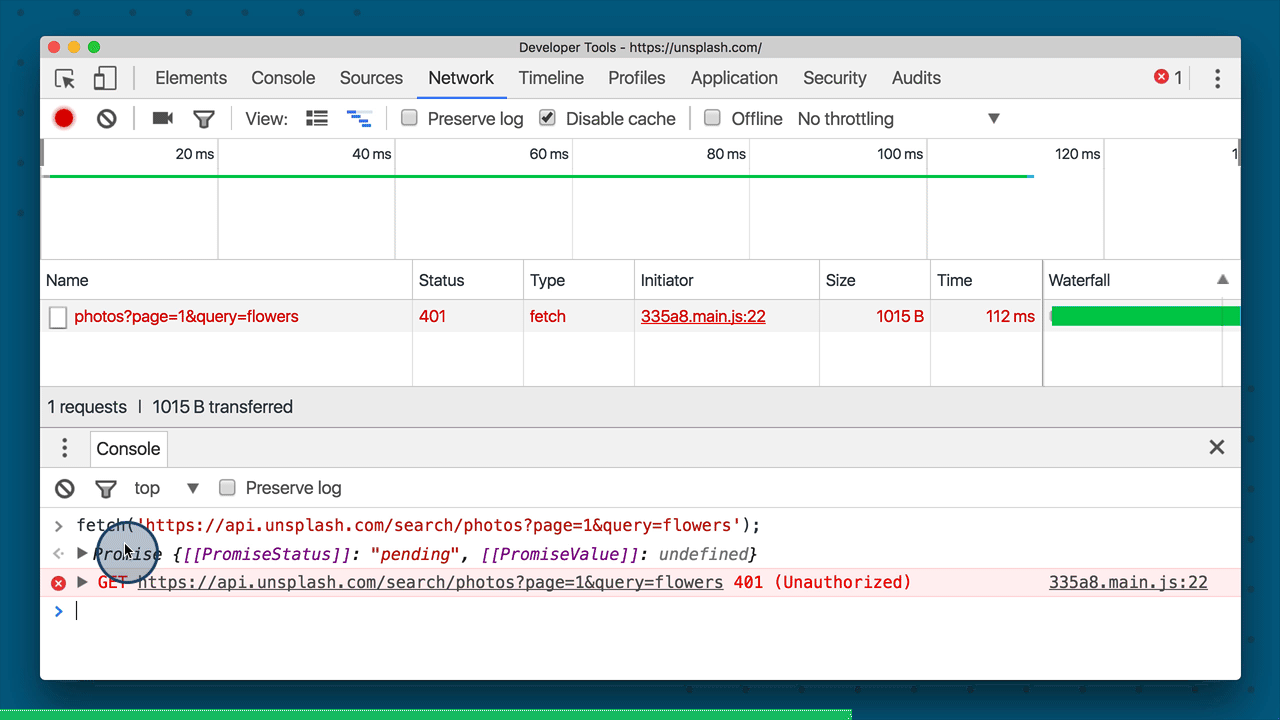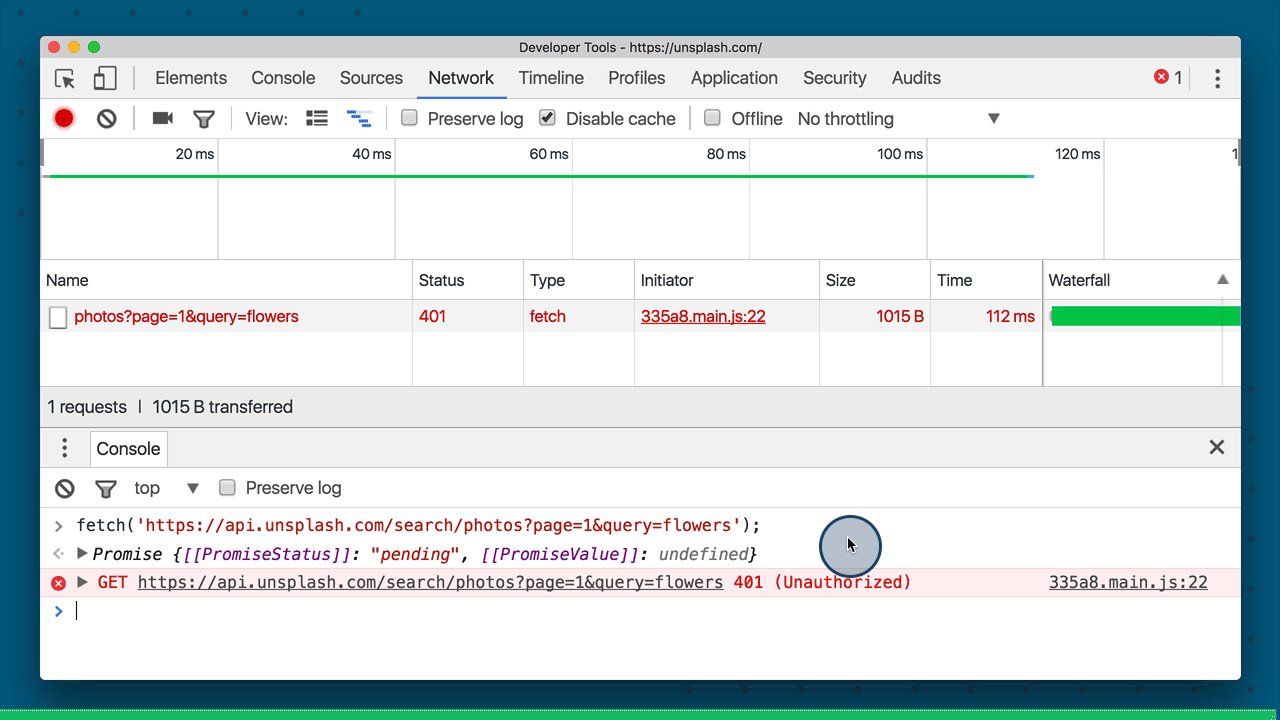
A fetch request being run on the console of Unsplash's website. The fetch request returns a Promise.
💡 Cross-Origin Issues? 💡
Did you just try running the Fetch request and it didn't work? Were you running it on Unsplash's website? If not, make sure you go to https://unsplash.com/, open the console, and try running it from there.
Just because Fetch is new and awesome and is replacing the XHR object for making asynchronous network requests doesn't mean it can bypass the rules for making those network requests. Fetch requests still need to obey the cross-origin protocol of how resources are shared. This means that, by default, you can only make requests for assets and data on the same domain as the site that will end up loading the data.
Remember that Unsplash requires an Authorization header to make a request through its API. Check out these links on Fetch's documentation to see how to add an Authorization header to the Fetch request.
Adding a Header to a Fetch Request
SOLUTION:
- fetch(`https://api.unsplash.com/search/photos?page=1&query=${searchedForText}`, {
headers: {
Authorization: 'Client-ID abc123'
}
}); - const requestHeaders = new Headers();
requestHeaders.append('Authorization', 'Client-ID abc123');
fetch(`https://api.unsplash.com/search/photos?page=1&query=${searchedForText}`, {
headers: requestHeaders
});
Get Or Post Request By Default
SOLUTION:
GETChanging The HTTP Method
So the default HTTP method for a Fetch request is the GET method. We can choose a different HTTP method by passing a method property in the configuration object:
fetch(`https://api.unsplash.com/search/photos?page=1&query=${searchedForText}`, {
method: 'POST'
});This will send the request with the POST HTTP header.
Fetch's specification does not limit what HTTP methods can be used, although it does recommend that all methods are written in uppercase for consistency with the HTTP Verbs specification.